Installation cost, aesthetics and energy generation efficiency differs from one type of solar panel to another. With that in mind, understanding what each type of solar panel has to offer will be beneficial in helping you decide which is best suited for your roof. Here’s absolutely everything you need to know about the different types of solar panels in Singapore.
What are the types of solar panels available in Singapore?
There are 3 main types of solar panels available in the Singapore solar market today. They’re monocrystalline, polycrystalline and thin-film solar panels. The market standard for solar panels in Singapore, however, are the monocrystalline solar panels due to their quality and efficiency.
Each type has its pros and cons and is made in its own unique way. Check your a quick summary of their differences below!
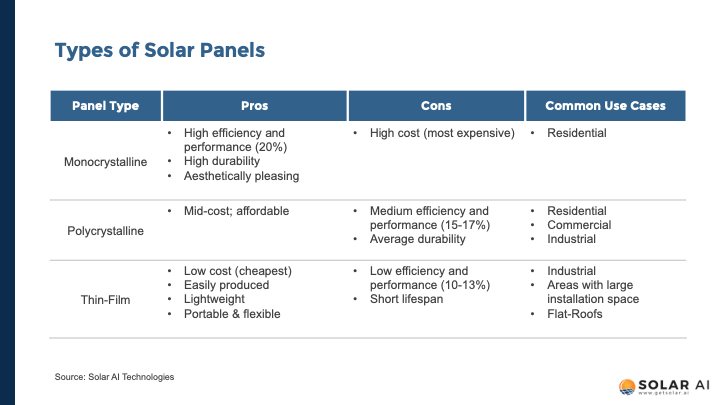
Traditional first-generation solar panels are usually made of monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon. On the other hand, second-generation ones, made using innovative technology, are thin-film solar panels.
Appearance
Given the different materials and manufacturing methods, the outer appearance of each type of solar panel is different. While some solar panels are black out-of-the-box, they can often appear to be blue or have a bluish hue when seen from a distance. This colour difference can generally be seen when light interacts with the panels. Let’s take a look at the different appearances of the panels!
Monocrystalline


The characteristic appearance of the monocrystalline solar panel is a dark or black exterior. The dark appearance is due to the way that sunlight interacts with the material of the solar panel. When sunlight traps sulfur atoms in the silicon it causes these solar panels to appear dark. Although you can’t change the colour of monocrystalline solar cells, their frames and back sheets are highly customisable. Pick from a range of designs and colours when you get solar panels of this type in Singapore. The most popular solar frame options are black and silver while the back sheets are commonly black, silver or white.
Additionally, monocrystalline panels are square-shaped, with rounded edges and their corners removed, causing small gaps between each cell.
Polycrystalline
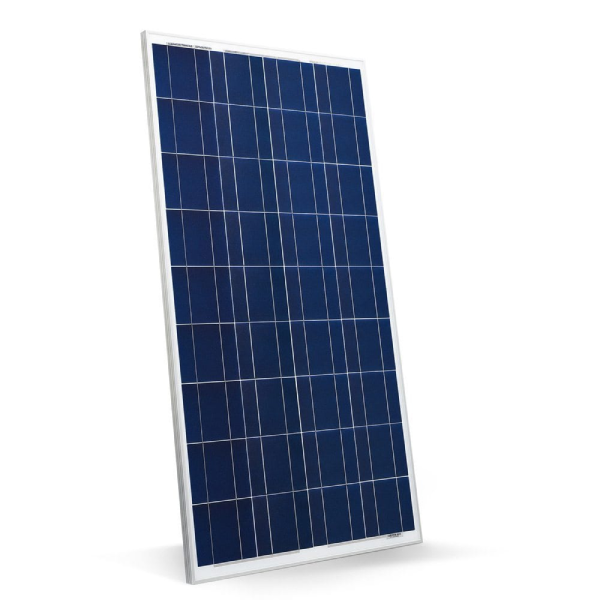


Unlike monocrystalline cells, polycrystalline cells are marbled and blue. Sunlight that reflects off the crystal fragments gives this type of solar panel a blue, speckled appearance. Just like monocrystalline cells, you can also choose from various different back sheet and frames for polycrystalline options. Often, the solar frames are silver and the back sheet is silver or white. Polycrystalline cells are also square with no gaps or spaces between them.
Thin-Film
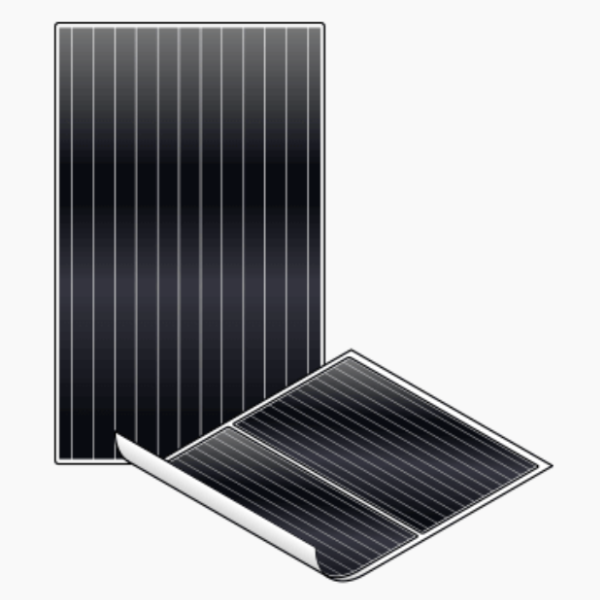


Thin-film solar panels tend to be solid black, but can also come in both blue and black shades, dependent on the material used during manufacturing. As the name suggests, they are significantly thinner compared to other solar panel types. Cells within the panels are approximately 350 times thinner than the crystal cells used in both monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. Its thinness is the greatest aesthetic advantage that it has over the other two solar panels.
Material of Solar Panels
Wondering how do solar panels work? Well, solar panels are made from a semiconductor material that converts light into electricity. Silicon is the most commonly used semiconducting material during the manufacturing process.
Monocrystalline & Polycrystalline
Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are made from silicon, specifically silicon wafers. These wafers are aligned and assembled forming a rectangular panel. Afterwhich, they’re coated with a glass sheet and mounted onto a metal frame.
While both types of solar panels are made from silicon, their manufacturing process and silicon composition are different. Monocrystalline panels are formed using the Czochralski method, by setting a pure silicon crystal into a tank of molten silicon at high temperature. The end result of this process is thinly sectioned silicon sheets or wafers. These sheets are then made into the solar cell and put together to form one solar panel.
On the other hand, polycrystalline panels are made from multiple crystals. Just like monocrystalline cells, a silicon crystal is placed into a tank of molten silicon. However, instead of removing the crystal, the silicon is left to fragment and cool. The cooling process will result in the formation of many crystals in the mould. Once cooled, the new fragmented crystal is sliced into wafers and assembled rectangularly to form a polycrystalline panel.
Thin-Film
Thin-Film solar panels are made with a variety of materials. They’re produced by placing a thin layer of one or more films of photovoltaic matter onto a solid substrate surface. Examples of these photovoltaic materials include silicon, cadmium, copper and dye-sensitised solar cells. The most widely available thin-film solar panel is made from cadmium telluride (CdTe). During manufacturing, a layer of CdTe will be placed between layers of transparent conductors to capture sunlight. A glass layer is placed on top of the other layers as protection.
While different types of materials result in different forms of solar panels, they still fall under the category of thin-film solar cells. Due to the simplicity of the manufacturing process, the panels tend to be lightweight and flexible.
Efficiency and Performance
Monocrystalline
Monocrystalline solar panels have the highest conversion efficiency at approximately 20%. This is because they contain the highest silicon purity among all solar panel types. These panels are crafted from a single silicon crystal, thereby allowing for faster electron flow between cells. They’re also more durable and can withstand higher temperatures, making them one of the most suitable types of solar panels in Singapore. Overall, these panels generally contain 60 to 72 solar cells and are some of the most efficient on the market.
Polycrystalline
For a polycrystalline solar panel, 60 to 72 solar cells are also needed to form one panel. Polycrystalline solar panels, while more affordable, are much less efficient in nature.
This is due to the fragmented nature of the silicon crystals, which makes it more difficult for electrons through each solar cell. This polycrystalline structure causes it to have a slightly lower conversion efficiency rate at around 15 to 17%.
Thin-Film
The thin-film technology has the lowest conversion efficiency of all solar panel technologies. The conversion efficiency rate of thin-film solar panels tends to be between 10 and 13%, regardless of the material used during manufacturing.
As thin-film technology doesn’t come in uniform sizes, the energy capacity of a thin-film solar panel system is largely dependent on the size of the panels. This means that to produce equal amounts of energy as monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panel setups, more thin-film solar panels are needed.
Cost
Monocrystalline
Due to the manufacturing process of monocrystalline solar panels, they’re significantly more expensive than other panels. This is because the entire process is energy-intensive and uses a pure silicon crystal which is expensive.
Polycrystalline
The manufacturing of polycrystalline solar panels involves melting pure whole silicon crystals. This is a faster and cheaper process compared to the Czochralski method used in monocrystalline panel production. Thus, these panels are more affordable. Due to their low cost, polycrystalline panels began making up a large portion of the market share for residential installations from 2012 to 2016.
However, as a result of the shorter lifespan and efficiency of polycrystalline panels, buyers have been going back to monocrystalline panels over the years.
Thin-Film
While they have low performance, thin-film panels are the least pricey. The ease of installation of these panels compared to the other panels also helps to further lower installation costs. However, they’re known to have shorter lifespans and degrade faster, which can mean that more frequent maintenance and replacements will be required.
So, which solar panel type is the best for you?
Choosing which panel is best for your installation depends on your property type and your specific needs. With each of these panels having its own pros and cons, it’s important to consider the space that you’ve got and the conversion efficiency you require to cover your daytime needs.
For us, we almost always recommend customers to purchase monocrystalline panels. This is because they’re space-efficient and can easily be installed onto residential rooftops. Also, they often have a long lifespan and function well beyond the given warranty period, which make them really great value for money.
We personally do not recommend polycrystalline panels, as it has a disproportionately low efficiency to its price, despite being budget. Additionally, polycrystalline solar panels require a much larger setup due to its low efficiency, which makes it much less worthy of a purchase.
Similarly, thin-film solar panels are completely different from first-generation solar panels. As the technology is still relatively new, they’re often not the best option for a residential solar installation. Mostly, they’re used in industrial solar installations, as the residential roofs are largely unable to withstand the weight of the large equipment required for the setup.
Before deciding on which solar panel is right for you, you should also check if your roof is suitable for installing solar panels. If you have a flat roof, thin-film solar panels would be suitable as they are flexible and can be modified into automatic panels. Automatic panels follow the sunlight throughout the day, maximising the amount of sunlight being absorbed. Although they’re less efficient compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, they may be able to produce more electricity on a flat roof.
This article was first published on 27 October 2020 and last updated on 16 August 2023 to include additional details.
Get an Instant Solar Estimate for your Property Now!
Whether you’re ready to install solar panels on your rooftop, or just wondering how you can benefit from solar, use our instant solar assessment tool to get an estimate of the solar potential of your property and find out how much you can save. At GetSolar, we combine geospatial analysis of satellite imagery with big data and artificial intelligence to provide you with reliable and accurate solar information so that you can make a better solar choice!